

Electric Vehicles
As we know Electric Vehicles (EVs) are those vehicles that run on electricity rather than a traditional gasoline, diesel, or petrol engine. Because they just have electric motors and batteries and emit no emissions at the exhaust, the EVs concept is made to be more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient than any traditional gasoline, petrol, or diesel internal combustion engine cars. the motors should be powered by renewable energy. these are important benefits of electric vehicles.
The bottom line is, electric vehicles are more than just a trend. They’re transforming the way we think about transportation and energy. So, whether you’re a car lover, an environmental enthusiast, or just someone who wants to save some bucks, it’s time to buckle up and embrace the electric ride. The future is electric, and it’s going to be electrifying!
Types Of Electric Vehicles
There are essentially four main types of electric vehicles available today. These include Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs). Let’s discuss a closer look at each of these.
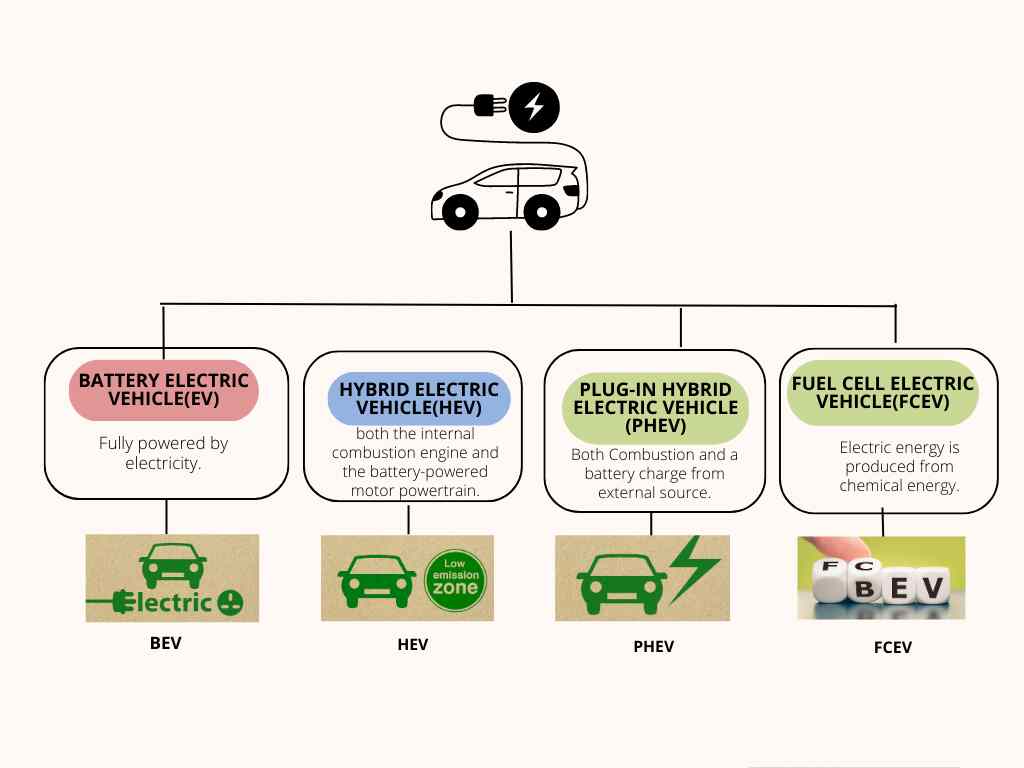

These are what most people think of when you say “electric vehicle.” BEVs are fully electric, meaning they rely solely on electricity for power. The battery, charged by plugging into an external power source, drives the electric motor. Because they run only on electricity, BEVs emit no tailpipe pollutants when driven. Some of the popular BEVs on the road today include the Tesla Model S, Nissan Leaf, and the BMW i3.
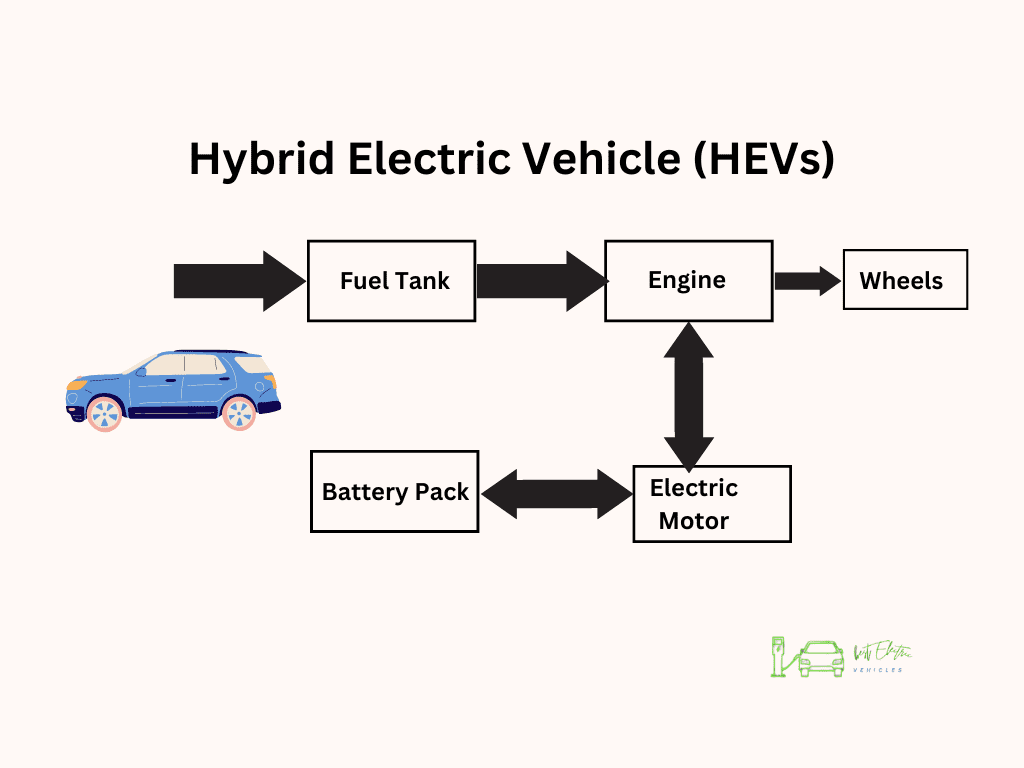
HEVs are like the middle ground between traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and BEVs. They combine an internal combustion engine with a battery and electric motor. These vehicles don’t need to be plugged in – energy is generated through regenerative braking and by the engine running. The Toyota Prius is probably the best-known example of a hybrid electric vehicle.
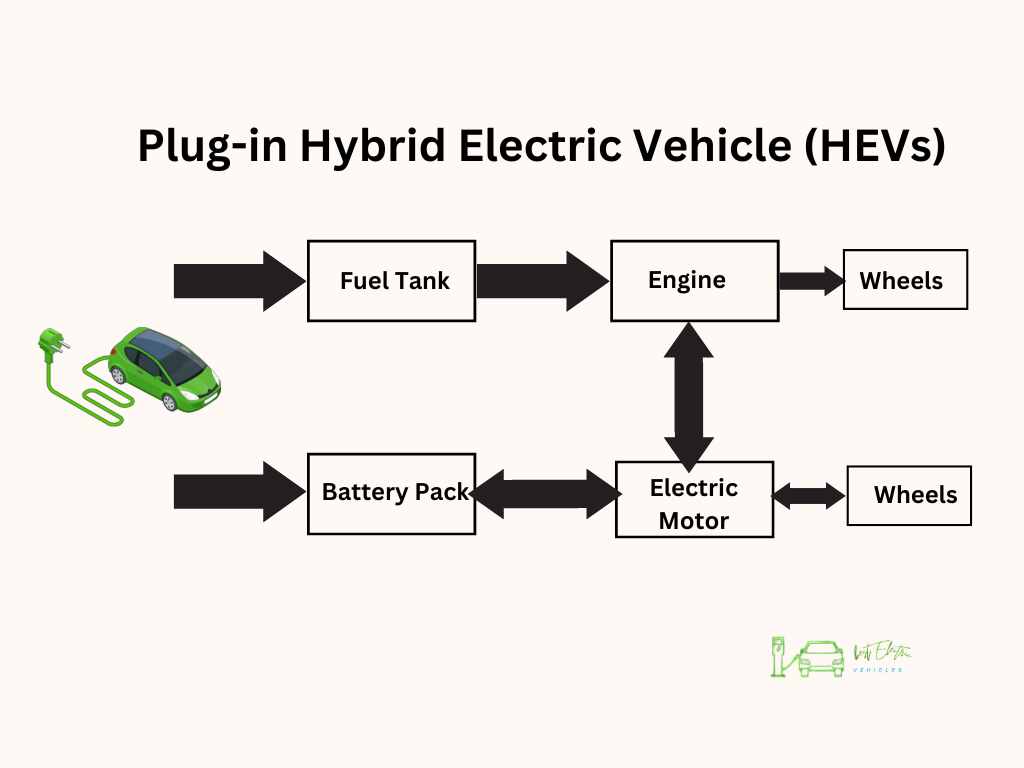
PHEVs are a sort of ‘best of both worlds’ scenario. They have a battery that can be charged by plugging into an external source, and they also have an internal combustion engine. The vehicle can run on electric power alone until the battery runs down. Then, the internal combustion engine kicks in, making them great for longer trips where charging may not be available. Examples of PHEVs include the Chevy Volt and the Ford Fusion Energine.

The magic happens inside a device called a fuel cell stack. The hydrogen gas stored in the vehicle’s tank combines with oxygen from the air inside the fuel cell stack. This chemical reaction generates electricity, which powers the motor that drives the vehicle. One great thing about this process is that the only by-product is water vapour, making FCEVs zero-emission vehicles just like Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs).

PROS AND CONS
1. Environmentally Friendly
2. Economical to Run
3. Quiet and Smooth Operation
4. Quick Acceleration and Responsive Handling
5. Quiet and Smooth Operation
6. Energy Efficiency
7. Decreased Dependence on Fossil Fuels
8. Government Incentives

1. Lack Of Infrastructure
2. High Battery Cost
3. Charging Time Should be Less
4. Expensive because of less Infrastructure
Battery (Auxiliary)
This denotes that the battery is used for secondary or supplementary functions. An auxiliary battery, on the other hand, might power non-propulsion systems such as lights, infotainment systems, air conditioning, and other electronic components.
In many cases, having a separate auxiliary battery can be beneficial because it ensures that essential functions (like lights or safety systems) can still operate even if the main battery is depleted or malfunctioning.
Onboard Charger
In the context of electric vehicles (EVs), an onboard charger refers to the device that converts alternating current (AC) from a wall outlet or charging station into direct current (DC) to charge the vehicle’s battery pack.
When an EV is plugged into a standard electrical outlet or a Level 1 or Level 2 charging station, it uses AC power. However, the batteries in EVs store and utilize DC power. The onboard charger’s primary function is to convert this AC power to DC power suitable for the battery, ensuring the battery is charged safely and efficiently.
It’s worth noting that when EVs use fast-charging stations (often referred to as Level 3 or DC fast chargers), the conversion from AC to DC typically happens outside the vehicle, so the onboard charger is bypassed in such scenarios.
Thermal System
The thermal system in an electric vehicle is responsible for maintaining the optimal temperature range for various components, especially the battery pack, to ensure safety, performance, and longevity.
Charging Port
Electric vehicles use specialized charging ports to recharge their batteries. The type of port often determines the speed at which the vehicle can be charged.
when considering an electric vehicle, it’s crucial to be aware of the charging standards the car supports, the availability of compatible charging stations in the area, and any adapters that might be necessary for broader charging access.
Traction Battery Pack
A traction battery pack, also known simply as a battery pack, is the set of batteries that power the electric motor in an electric vehicle (EV) or a hybrid vehicle.
the traction battery pack is the heart of an electric vehicle, determining its range, performance, and a significant portion of its cost.
Transmission
In the context of electric vehicles (EVs), “transmission” typically refers to the system responsible for transmitting power from the electric motor to the wheels to propel the vehicle forward or backward.
DC/DC Converter
the DC/DC converter in an electric vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining the vehicle’s electrical systems by converting the high-voltage DC power from the main battery into the lower-voltage DC power needed for auxiliary systems. It provides electrical isolation, efficient voltage adaptation, and ensures the operation of critical systems, contributing to the overall functionality and safety of the EV.
Power Controller
Power controllers are often used to control the speed, direction, and torque of electric motors.
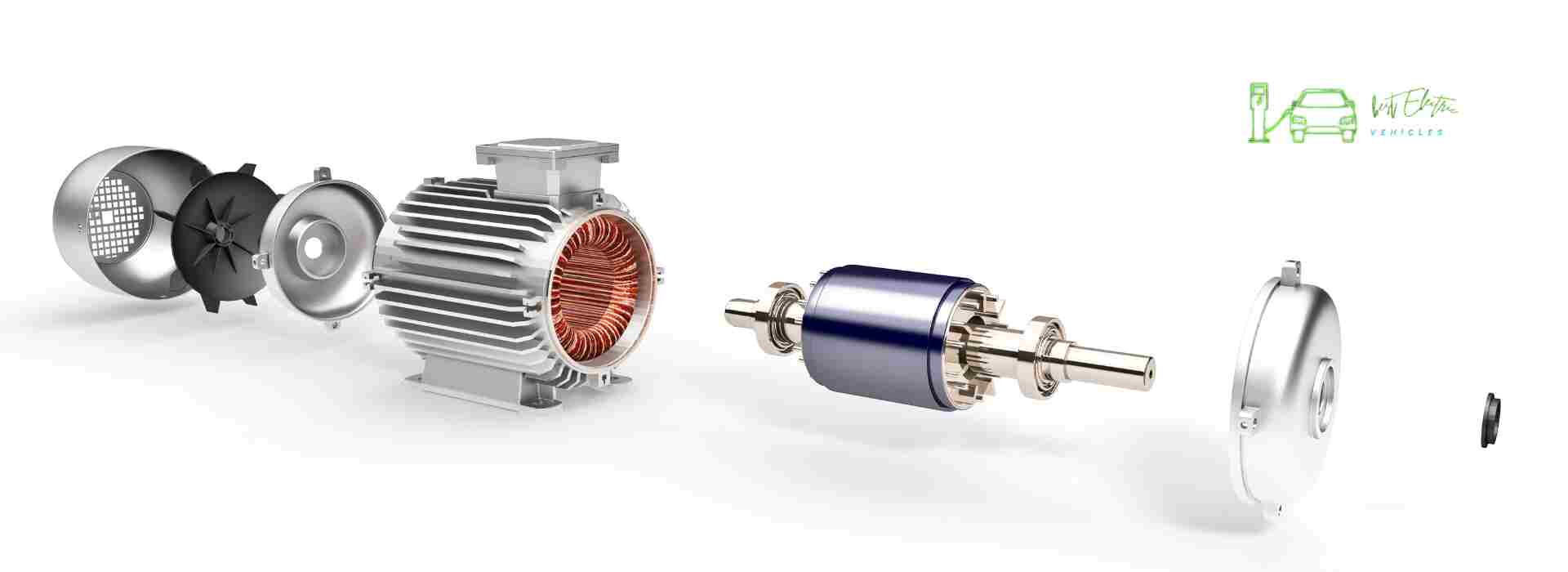
Electric Traction Motor
Electric traction motors play a critical role in electric vehicles (EVs) as they are responsible for converting electrical energy from the vehicle’s battery into mechanical energy to drive the wheels.
Why VOLCON GRUNT EVO is Dominating 2024: An Insider’s Guide
In the ever-evolving landscape of cutting-edge technology, there is one name in…
The TVS iQube Scooter: Why It’s the Tesla of Two-Wheelers!
TVS iQube is the latest modern electric scooter which is rapidly gaining…
Toyota’s Electric Dream: A Closer Look at the SUV That’s Making Tata Tremble
Toyota Kirloskar Motor has recently unveiled a groundbreaking electric SUV in the…
Volcon Brat Electric Vehicle (VBEV)
With time, our automobile engineers have surprised the whole world by inventing…
How does an electric motor function?
We all know that an electric motor machine has a stationary part,…
Lightning on 4 Wheels: The Rise of Electric Cars in India!
Ever paused mid-scroll on your social media feed, captivated by a sleek,…







